When it comes to technical analysis in trading, the Relative Strength Index (RSI) is one of the most commonly used indicators. Traders often rely on RSI to understand whether an asset is overbought or oversold, and to identify potential reversals in trends. It’s a powerful tool that can help traders make well-timed entry and exit decisions. But how exactly do you use RSI to generate trading signals? Let’s break it down step by step.
Relative Strength Index (RSI) for Trading Signals If you want to read same article in hindi click here
Understanding the Basics of RSI
RSI is a momentum oscillator that measures the speed and change of price movements. It’s plotted on a scale from 0 to 100, providing an easy way to visualize when an asset might be reaching a point of reversal.
The formula behind RSI
RSI is calculated using the following formula:
[
RSI = 100 – \left(\frac{100}{1 + RS}\right)
]
Where RS (Relative Strength) is the average gain of up periods divided by the average loss of down periods, usually over a 14-period timeframe. This helps smooth out price fluctuations and provides insight into whether a stock is experiencing more gains or losses in recent trading periods.
RSI scale: 0 to 100
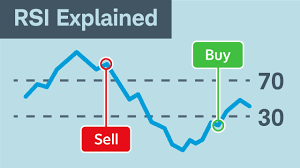
The RSI value oscillates between 0 and 100. Values above 70 typically indicate that an asset is overbought, while values below 30 suggest that it may be oversold. These key levels form the foundation of RSI trading signals.
Interpreting RSI for Overbought and Oversold Conditions
One of the most basic uses of RSI is identifying overbought and oversold conditions.
What does overbought mean?
When RSI rises above 70, it suggests that an asset has been rising too quickly and may be due for a pullback. In other words, it’s considered overbought. Traders often take this as a signal to sell or at least prepare for a price drop.
What does oversold mean?
Conversely, when RSI falls below 30, it indicates that the asset has been selling off too quickly and may be due for a bounce back. This condition is called oversold, and traders often see it as a buying opportunity.
How to trade in overbought conditions
When an asset’s RSI crosses the 70 mark, it’s a signal that the asset may be reaching its peak. Traders often look for confirmation signals before taking action, such as declining volume or other technical indicators.
How to trade in oversold conditions
When RSI drops below 30, it indicates a potential buying opportunity as the asset is oversold. Traders can look for other indicators like support levels or a bullish candlestick pattern before making a move.
RSI Divergence: A Powerful Trading Signal
RSI divergence is one of the most reliable signals RSI can generate. It happens when the price of an asset moves in the opposite direction of the RSI, signaling a potential trend reversal.
Identifying bullish divergence
A bullish divergence occurs when the price makes lower lows, but the RSI makes higher lows. This indicates that even though the price is falling, the underlying momentum is building up, signaling a potential reversal to the upside.
Identifying bearish divergence
A bearish divergence happens when the price makes higher highs, but the RSI makes lower highs. This suggests that although the price is rising, the momentum is weakening, and a downward reversal may be near.
RSI and Different Time Frames
The RSI can be adapted for different time frames, making it useful for various trading styles.
Intraday traders vs. swing traders
Intraday traders often use shorter time frames like the 5-minute or 15-minute RSI, while swing traders might look at the daily RSI. Day traders benefit from quicker signals but need to be cautious of increased market noise.
Long-term investors and RSI
Long-term investors often focus on weekly or monthly RSI, which helps smooth out short-term volatility and provides a clearer picture of overall trends.
Combining RSI with Other Indicators for Stronger Signals
While RSI is a powerful tool, it’s even more effective when combined with other technical indicators.
RSI and Moving Averages
Combining RSI with Moving Averages (MA) helps confirm trends. For instance, if RSI indicates that a stock is oversold, and the price is bouncing off a 200-day moving average, it could be a strong buy signal.
RSI and MACD
The Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD) indicator can filter false signals generated by RSI. If both RSI and MACD signal a reversal, it can give traders more confidence to take action.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Using RSI
Using RSI without proper understanding can lead to mistakes.
Ignoring longer trends
RSI is a short-term indicator, so ignoring the broader trend can lead to false signals. It’s important to consider the overall market context.
Over-relying on RSI without confirmation
RSI should not be used in isolation. Always confirm RSI signals with other indicators or price action analysis to avoid potential losses.
RSI-Based Trading Strategies
There are several strategies you can employ using RSI.
RSI bounce strategy
In this strategy, traders buy when RSI hits oversold levels and sell when RSI reaches overbought levels. This is most effective in range-bound markets where prices bounce between support and resistance levels.
RSI failure swing strategy
The failure swing is a reversal pattern that forms when the RSI breaks through previous support or resistance levels. Traders can capitalize on these breakouts for potentially large price moves.
Conclusion
The Relative Strength Index (RSI) is an essential tool for traders seeking to identify overbought and oversold conditions, as well as potential trend reversals. By understanding how to use RSI effectively and combining it with other technical indicators, you can improve your trading signals and make more informed decisions. Remember, no single indicator is foolproof, so always practice proper risk management and use multiple sources of confirmation.
How to Use Moving Averages in Technical Analysis
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Can RSI be used in all types of markets?
Yes, RSI can be applied to any market, including stocks, forex, commodities, and cryptocurrencies.
2. What is the best period to set for RSI?
The standard setting for RSI is 14 periods, but some traders adjust this based on their strategy, using shorter periods for quicker signals or longer periods for smoother trends.
3. How often should I check RSI during the trading day?
It depends on your trading style. Day traders may check RSI frequently, while swing traders might only review it at key times during the trading session.
4. Is RSI better suited for stocks or forex?
RSI works well for both, but it is especially useful in highly liquid markets like forex and stocks.
5. Can RSI be applied to cryptocurrency markets?
Yes, RSI can be very useful in crypto trading, particularly due to the high volatility of the market, which often leads to overbought and oversold conditions.

1 thought on “How to Use the Relative Strength Index (RSI) for Trading Signals”