Introduction to Swing Trading
Swing trading is a popular trading style that seeks to capture short- to medium-term gains in a stock (or any financial instrument) over a few days to several weeks. Unlike day trading, where traders buy and sell stocks within a single day, swing trading focuses on holding positions for multiple days to take advantage of anticipated market shifts. But what makes swing trading such an attractive strategy for traders? Let’s dive into the details.
If you want to read same article in hindi click here
Understanding the Stock Market for Swing Trading
Before diving into swing trading, it’s important to understand the stock market’s fundamentals. The stock market operates in cycles — periods of growth followed by corrections or declines. Knowing these cycles and the trends within them is essential for swing traders.
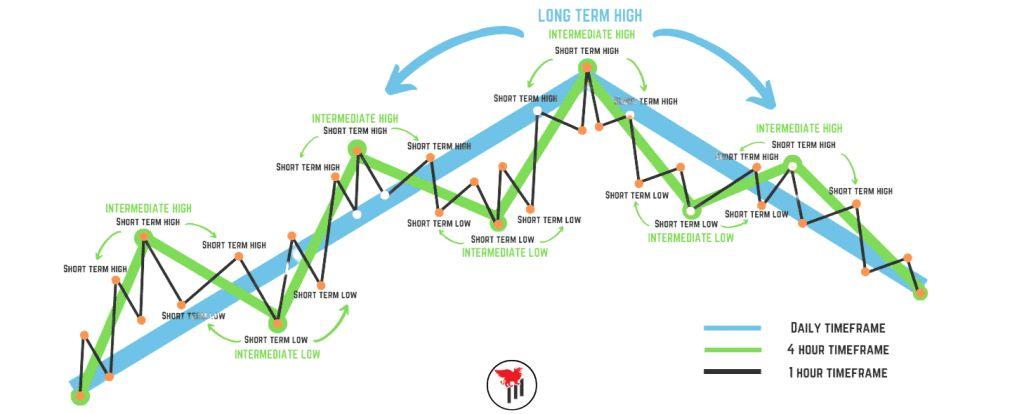
Market Cycles and Trends
Swing traders rely heavily on understanding market cycles, which are fluctuations in stock prices influenced by economic factors, market sentiment, and technical patterns. Recognizing these trends helps traders enter and exit trades at optimal times.
Key Terminology for Swing Traders
To succeed in swing trading, you need to understand key terms like support and resistance, bullish and bearish trends, and moving averages. These concepts form the basis for most swing trading strategies.
Difference Between Swing Trading and Day Trading
Swing trading and day trading are often confused, but they differ in several key aspects.
Time Frame Comparison
Day trading involves buying and selling stocks within a single day, while swing trading holds positions from a few days to several weeks. Swing trading allows for more flexibility in timing and often requires less time commitment than day trading.
Risk and Reward Differences
Day trading can offer quick profits but comes with higher risk due to its fast pace. Swing trading, while still risky, typically involves lower risk per trade because it allows traders more time to make decisions based on thorough analysis.
Tools and Resources Needed for Swing Trading
Swing traders rely on various tools to analyze markets and execute trades efficiently.
Trading Platforms and Software
Platforms like MetaTrader, Thinkorswim, and TradingView provide real-time data, charting tools, and advanced features for executing trades.
Charting Tools and Indicators
Tools like Bollinger Bands, Moving Averages, and the Relative Strength Index (RSI) help traders predict stock price movements and identify profitable opportunities.
News and Information Sources
Swing traders must stay updated with financial news. Platforms like Bloomberg, Reuters, and stock-specific news aggregators can provide real-time insights that affect market movements.
How to Identify Swing Trading Opportunities
Finding the right opportunities is critical in swing trading.
Technical Analysis Basics
Swing traders heavily rely on technical analysis, which involves studying charts and price patterns. Key metrics like candlestick patterns, moving averages, and volume indicators help identify when to enter or exit a trade.
Fundamental Analysis and Its Role
While technical analysis is more common in swing trading, fundamental analysis (e.g., analyzing a company’s earnings reports, industry trends) also plays a role in long-term predictions.
Importance of Volume and Volatility
Stocks with higher volume (number of shares traded) and volatility (price fluctuations) are ideal for swing trading because they provide more trading opportunities within short time frames.
Popular Swing Trading Strategies
There are several tried-and-tested strategies that swing traders often use.
Moving Averages Strategy
The moving average strategy helps identify trends by smoothing out stock prices over time, making it easier to spot upward or downward trends.
Support and Resistance Strategy
This strategy involves identifying price levels where a stock has repeatedly bounced up or down, known as support (lower level) and resistance (upper level).
Breakout Trading Strategy
A breakout occurs when a stock price moves beyond a support or resistance level, signaling the potential for strong upward or downward momentum.
RSI (Relative Strength Index) Strategy
RSI is a momentum indicator that measures the speed and change of price movements, often signaling when a stock is overbought or oversold.
Managing Risk in Swing Trading
Risk management is crucial to long-term success in swing trading.
Importance of Stop-Loss Orders
A stop-loss order automatically sells your stock if it reaches a certain price, helping you minimize losses in volatile markets.
Position Sizing and Diversification
Effective position sizing (deciding how much to invest in each trade) and diversifying your investments reduce the risk of any single trade impacting your entire portfolio.
Emotional Control and Discipline
It’s easy to get emotional when markets move unpredictably. Successful traders maintain discipline and follow their strategies, regardless of market fluctuations.
Executing Trades and Timing the Market
Timing is everything in swing trading.
Entry and Exit Points
Identifying the right entry and exit points ensures that you buy low and sell high, maximizing profits while minimizing losses.
Timing the Market with Technical Indicators
Indicators like the moving average convergence divergence (MACD) and stochastic oscillators help traders pinpoint the ideal moments to enter or exit trades.
The Psychology of a Successful Swing Trader
Mastering swing trading isn’t just about strategies; it’s about mindset.
Developing a Mindset for Success
Swing trading requires patience, confidence, and a level-headed approach. Emotional decisions often lead to mistakes.
Patience and Emotional Balance
You must be willing to wait for the right setup and avoid emotional trading, which can lead to overtrading or holding onto losing positions for too long.
Common Mistakes Swing Traders Make
Even experienced traders make mistakes. Here are some common pitfalls:
Overtrading
Trading too frequently can lead to losses due to higher fees and emotional decision-making.
Ignoring Risk Management
Many traders focus too much on profits and ignore the importance of limiting their potential losses through proper risk management techniques.
Focusing Only on Profits
Swing trading isn’t about hitting a home run on every trade. It’s about steady, consistent profits over time.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Swing Trading
Swing trading has both upsides and downsides.
Benefits of Swing Trading
Swing trading offers more flexibility than day trading and allows traders to capitalize on market movements without having to monitor markets constantly.
Challenges and Risks Involved
However, the risk of loss is always present, and external market factors (such as news events) can impact stock prices overnight, adding an element of uncertainty.
How to Backtest a Swing Trading Strategy
Backtesting involves testing a trading strategy on historical data to see how it would have performed.
Importance of Backtesting
Backtesting allows traders to evaluate the effectiveness of their strategies and make necessary adjustments before risking real money.
**Step-by
-Step Guide to Backtesting**
- Choose a specific stock or set of stocks.
- Apply your trading strategy to historical data.
- Analyze the results and refine your strategy.
Swing Trading for Beginners: Starting Small
For those new to swing trading, it’s important to start small and gradually scale up.
How to Build a Small Account with Swing Trading
By focusing on small but consistent gains, new traders can build their accounts without risking too much capital.
Learning from Mistakes and Adjusting Strategies
Mistakes are inevitable, but they provide valuable lessons for improving your trading strategy over time.
Tax Implications of Swing Trading
Swing trading is subject to taxes, particularly on short-term gains.
Short-Term Capital Gains Tax
Profits from trades held for less than a year are taxed as short-term capital gains, which are usually higher than long-term gains.
Reporting and Filing Your Swing Trading Taxes
Accurate record-keeping is essential for tax season. Consult a tax professional to ensure you’re reporting your trades correctly.
Conclusion and Final Thoughts
Swing trading can be an excellent way to profit from short-term market movements. However, it requires a good understanding of technical analysis, strong risk management skills, and emotional discipline. By employing the right strategies and continually learning from both successes and mistakes, you can improve your chances of making consistent profits through swing trading.
How to Create a Winning Trading Plan
FAQs About Swing Trading
1. What is the ideal time frame for swing trading?
The ideal time frame typically ranges from a few days to a few weeks, depending on market conditions and your trading strategy.
2. Can swing trading be done part-time?
Yes, swing trading can be done part-time, making it an attractive option for those who cannot commit to full-time trading.
3. How much capital is required to start swing trading?
You can start swing trading with a relatively small amount of capital, but many recommend at least $2,000–$5,000 to cover potential losses and trading fees.
4. How do I choose the best stocks for swing trading?
Look for stocks with high liquidity, volatility, and clear technical patterns like support and resistance levels.
5. What are the best tools for swing traders?
Some of the best tools include charting software (like TradingView), news aggregators, and technical indicators such as the RSI and MACD.


1 thought on “How to Swing Trade Stocks for Short-Term Profits”