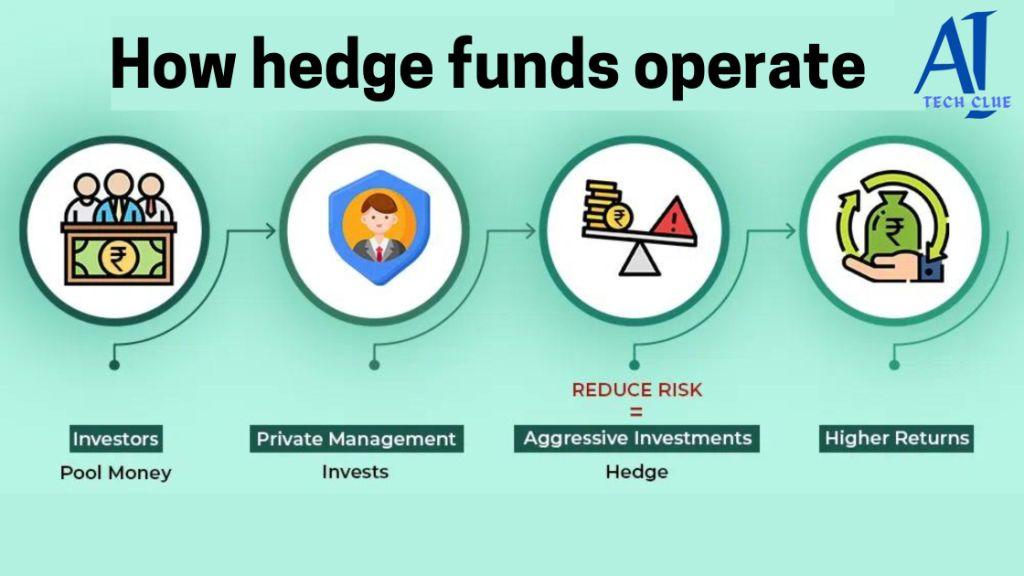
Hedge funds are often seen as mysterious and exclusive financial institutions. While they can seem complex, understanding how hedge funds operate can demystify their role in the financial world. In this article, we’ll take a detailed look at how hedge funds function, the strategies they employ, and the regulations that govern them.
If you want to read same article in hindi click here
What Are Hedge Funds?
Hedge funds are alternative investment vehicles that pool capital from high-net-worth individuals or institutional investors to generate returns. Unlike mutual funds or exchange-traded funds (ETFs), hedge funds have more flexibility in the strategies they use, including short selling, leveraging, and derivatives trading. This flexibility allows them to potentially earn returns regardless of market conditions.
The Origins of Hedge Funds
The first hedge fund is often attributed to Alfred Winslow Jones, a sociologist turned financial journalist, who established it in 1949. His approach was to “hedge” market risk by balancing long and short positions, which set the foundation for modern hedge funds.
How Hedge Funds Differ From Other Investment Vehicles
Hedge Funds vs. Mutual Funds
While both hedge funds and mutual funds pool investors’ money to invest in a variety of assets, they differ significantly in their structure and strategies. Mutual funds are heavily regulated, with restrictions on short selling and leverage. Hedge funds, on the other hand, have fewer constraints, allowing them to take on higher risks in pursuit of greater returns.
Hedge Funds vs. ETFs
ETFs (Exchange-Traded Funds) are designed to track the performance of a particular index or sector, offering more transparency and liquidity than hedge funds. Hedge funds, by contrast, often aim for absolute returns and are not restricted by an index, giving managers broader discretion.
Types of Hedge Fund Strategies
Hedge funds use a wide variety of strategies, each tailored to different market conditions and investor preferences. Below are some of the most common strategies employed by hedge funds:
Long/Short Equity
In this strategy, hedge funds take long positions in undervalued stocks and short positions in overvalued ones. By balancing the two, they aim to reduce overall market risk while generating returns.
Event-Driven Strategy
Event-driven strategies focus on corporate events like mergers, acquisitions, or bankruptcies. Hedge funds invest in companies undergoing significant transitions, profiting from price fluctuations tied to these events.
Global Macro
This strategy involves betting on macroeconomic trends such as interest rates, currencies, or geopolitical events. Hedge funds using this approach typically invest across multiple asset classes, from stocks to bonds and commodities.
Quantitative Hedge Funds
Quantitative hedge funds rely on mathematical models and algorithms to identify trading opportunities. These funds often use high-frequency trading techniques, executing large numbers of trades at lightning speed.
The Structure of Hedge Funds
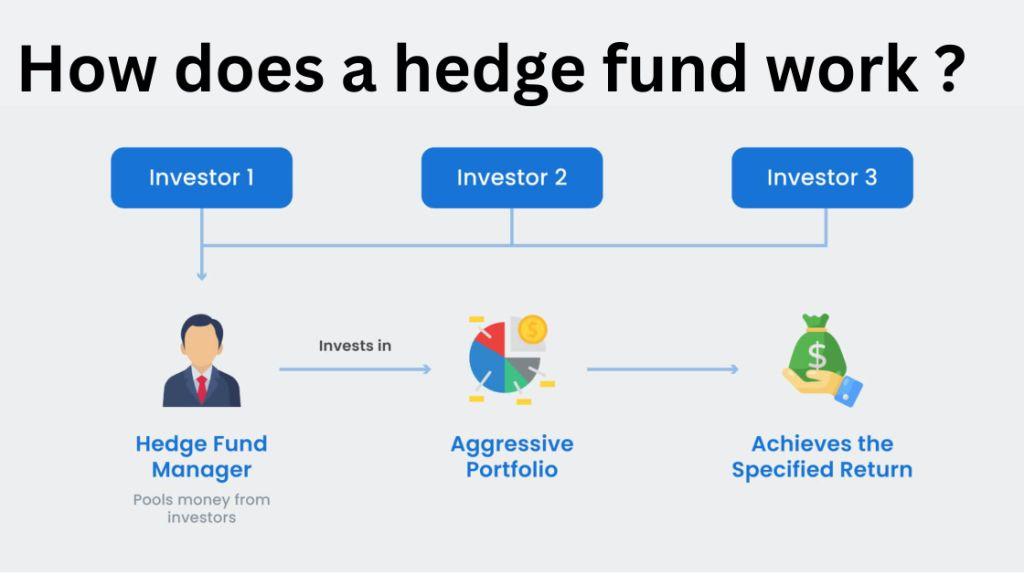
Hedge funds typically follow a two-tier structure composed of general partners (the fund managers) and limited partners (the investors). This structure is critical to understanding how hedge funds operate.
Fund Managers and Their Roles
Fund managers are responsible for making investment decisions and managing the day-to-day operations of the hedge fund. They typically receive a management fee, which is a percentage of the total assets under management (AUM), and a performance fee based on the profits earned.
Investors and Limited Partnerships
Investors in hedge funds are usually high-net-worth individuals or institutional investors like pension funds and endowments. These investors are known as limited partners and typically do not participate in the fund’s daily operations.
Performance Fees and Management Fees
Hedge funds often follow a “2 and 20” fee structure. This means a 2% management fee and a 20% performance fee on any profits above a predetermined threshold, providing a strong incentive for fund managers to deliver high returns.
How Hedge Funds Make Money
Hedge funds employ several methods to generate profits, often taking advantage of sophisticated strategies that other investment vehicles avoid.
Arbitrage Opportunities
One way hedge funds profit is by exploiting price discrepancies in different markets. Arbitrage strategies involve buying an asset in one market while simultaneously selling it in another, capitalizing on the price difference.
Short Selling Explained
Short selling involves borrowing a stock, selling it at the current price, and then buying it back at a lower price to return to the lender. This is a key tactic used by hedge funds to profit in declining markets.
Derivatives and Leverage
Hedge funds frequently use derivatives like options and futures to amplify their positions. Leverage, or borrowing money to increase the size of an investment, can enhance returns but also increases risk.
Hedge Fund Regulations and Legal Framework
The Role of the SEC (U.S.)
In the U.S., hedge funds are subject to oversight by the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC). Although they are less regulated than mutual funds, they must still adhere to certain guidelines, especially around investor protection and transparency.
Offshore Hedge Funds and Their Benefits
Many hedge funds operate offshore, in locations like the Cayman Islands or Bermuda, to benefit from favorable tax laws and less stringent regulations. This can provide operational flexibility but also invites greater scrutiny.
Recent Regulatory Changes
In recent years, hedge funds have faced increasing regulatory pressure, particularly in light of the financial crisis of 2008 and the growing use of complex derivatives. Compliance with new regulations can add operational costs but is necessary to protect investors.
The Role of Technology in Hedge Funds
Algorithmic Trading
Algorithmic trading allows hedge funds to execute large volumes of trades with precision, leveraging complex mathematical models to capture market inefficiencies.
The Impact of Artificial Intelligence
AI and machine learning are transforming the hedge fund industry by improving data analysis and decision-making, allowing fund managers to anticipate market trends with greater accuracy.
Risk Management in Hedge Funds
Risk management is crucial in hedge funds, given their high-risk strategies. Effective risk management practices are essential to protect against market volatility and losses.
Diversification Techniques
Hedge funds use diversification to spread risk across multiple asset classes, sectors, or geographic regions, reducing the likelihood of significant losses.
Risk Adjusted Returns
Hedge funds focus on achieving risk-adjusted returns, meaning they aim to generate the highest possible return for the level of risk taken. This ensures a balanced approach to investing, especially in uncertain markets.
Challenges Facing Hedge Funds Today
Market Volatility
Market volatility poses a significant challenge to hedge funds, as sudden shifts can impact even the most carefully crafted strategies.
Regulatory Scrutiny
Hedge funds are facing more stringent regulations, especially concerning transparency and risk management. This increased scrutiny can limit their operational flexibility.
The Future of Hedge Funds
The Impact of ESG (Environmental, Social, Governance) Investing
ESG investing is becoming increasingly important, and hedge funds are starting to adopt ESG criteria into their strategies to meet the demand for socially responsible investing.
Hedge Funds in a Post-COVID World
The COVID-19 pandemic has shifted market dynamics, and hedge funds are adapting to these changes. The future of hedge funds may involve more agile strategies to navigate a rapidly changing economic landscape.
Conclusion
Hedge funds play a significant role in today’s financial markets, offering both opportunities and risks. With their ability to employ sophisticated strategies and generate returns in various market conditions, hedge funds remain a popular choice for wealthy individuals and institutional investors. However, the complexities involved in hedge fund operations, coupled with increasing regulations, mean they are not without challenges.
How to Invest in Index Funds for Long-Term Growth
FAQs
What makes hedge funds different from mutual funds?
Hedge funds use more aggressive strategies like short selling and leverage, whereas mutual funds
are more regulated and focus on long-only positions.
Are hedge funds riskier than other investments?
Yes, hedge funds often take on more risk to achieve higher returns, making them riskier than traditional investment vehicles like mutual funds or ETFs.
How do hedge funds protect against losses?
Hedge funds employ various risk management techniques, including diversification, hedging, and the use of derivatives.
Can anyone invest in a hedge fund?
No, hedge funds are typically limited to accredited investors with significant financial resources due to their higher risk profile.
How do hedge funds influence the overall market?
Hedge funds can move markets, especially through strategies like short selling and arbitrage, which can create price volatility in certain assets.